GLASS FIBER VS STEEL
GLASS FIBER VS STEEL
ADVANCED MATERIAL
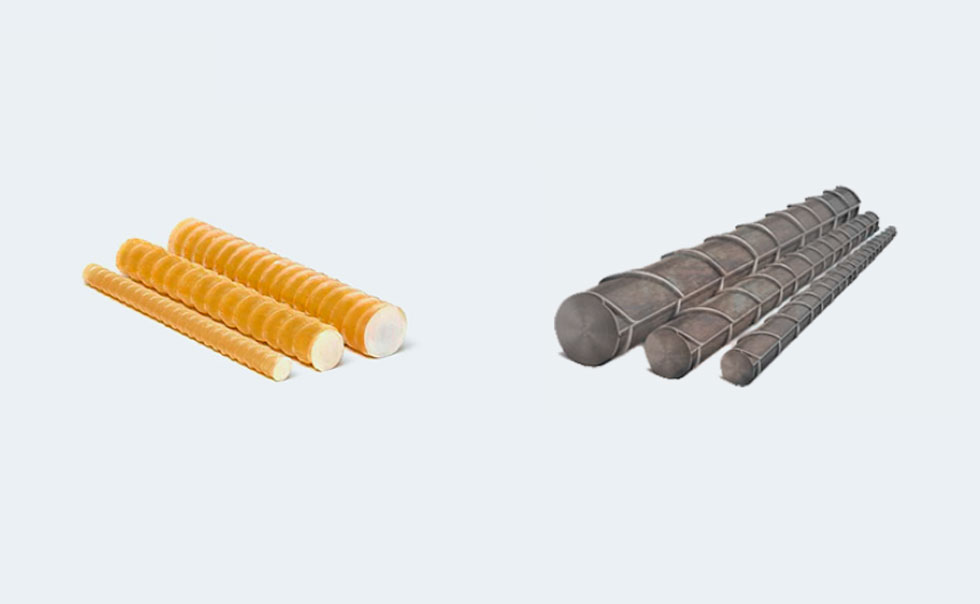
Glass fiber reinforcement is currently one of the most advanced materials in construction worldwide. Its popularity is due to the numerous advantages it offers compared to steel reinforcement. While concrete has high compressive strength, its tensile strength is relatively low. To compensate for this, reinforcement is used. Steel is still the most commonly used material for this purpose.
However, steel is susceptible to rust. Especially in areas where it lacks sufficient coverage, allowing moisture and salts to reach the steel and cause corrosion. Inadequate coverage is not the only issue; execution flaws or failure to use the correct spacers, which can lead to the reinforcement being too close to the exterior, can also accelerate corrosion.
Glass fiber reinforcement does not rust, is much lighter than steel, and has higher tensile strength.
These advantages alone contribute to its popularity among professional contractors. Nonetheless, many specialists still use traditional steel and hesitate to switch to glass fiber reinforcement. This hesitation is often due to a lack of information or insufficient understanding of the benefits of glass fiber reinforcement.
THE TEST: GLASS FIBER VS. STEEL
In this footage, it is clearly shown that an element reinforced with steel breaks at a certain point, while the element with glass fiber reinforcement bends further without breaking and, after the weight is removed, returns to its original shape.
Glass fiber reinforcement
Steel reinforcement
CROSS-SECTION OF CONCRETE SLABS
Tests have been conducted with fiberglass reinforcement meshes at a concrete slab manufacturer. Tests with glass fiber reinforcement meshes were conducted at a concrete slab manufacturer. In photos 1, 2, and 3, you can clearly see the steel bars with rust formation:
In photos 4 and 5, you can see the glass fiber reinforcement mesh. It’s clearly visible that it is not susceptible to corrosion. It is clear that these are not subject to corrosion:
Characteristics
| Characteristic | Glass fiber reinforcement | Steel reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Woven glass tape fully impregnated in thermosetting resin | Steel |
| Diameter tolerance | 0,1 mm +/- | 0,5 mm +/- |
| Density | 1900 – 2000 kg/m3 | 7800 kg/m3 |
| Strain in % | 2.2 | 25 |
| Fiber volume content | 70% fiber | 99% steel |
| Young’s modolus | 50.000 | 200.000 |
| E-modolus | 50 Gpa | 210 Gpa |
| compressive strength | 690 Mpa | |
| tensile strength | 1000 Mpa | 250 Mpa |
| short-term shear strength | 50 Mpa | |
| double shear strength | 150 Mpa | |
| thermal expansion coefficient – length | 9×10-6/C | |
| thermal expansion coefficient – transverse | 52×10-6/C | |
| components | 70% ECR glass fiber with epoxy resin | steel with PE protective layer 0.3 mm |
| Corrosion resistant | Yes | No |
| Density kg/m3 | 1900 (4 times lighter than steel) | 7800 |
| Environment | For every ton of steel produced, 1.9 tons of CO2 are emitted | |
| yield moment | It is higher than that of steel | |
| Higher tensile strength | 600-1600 N/mm2 | 200-550 N/mm2 |
| Resistant to chloride and phosphate | Yes | No |
| Conducts radio waves | Yes | No |
| Thermal conductivity | 0,25% | 48% to 58% |
| Diamagnetic | Yes | No |
| Durability | Expected durability: 80 years | According to building regulations |
See Also: